India's Macroeconomic Overview 2025: A Bright Spot in Global Growth
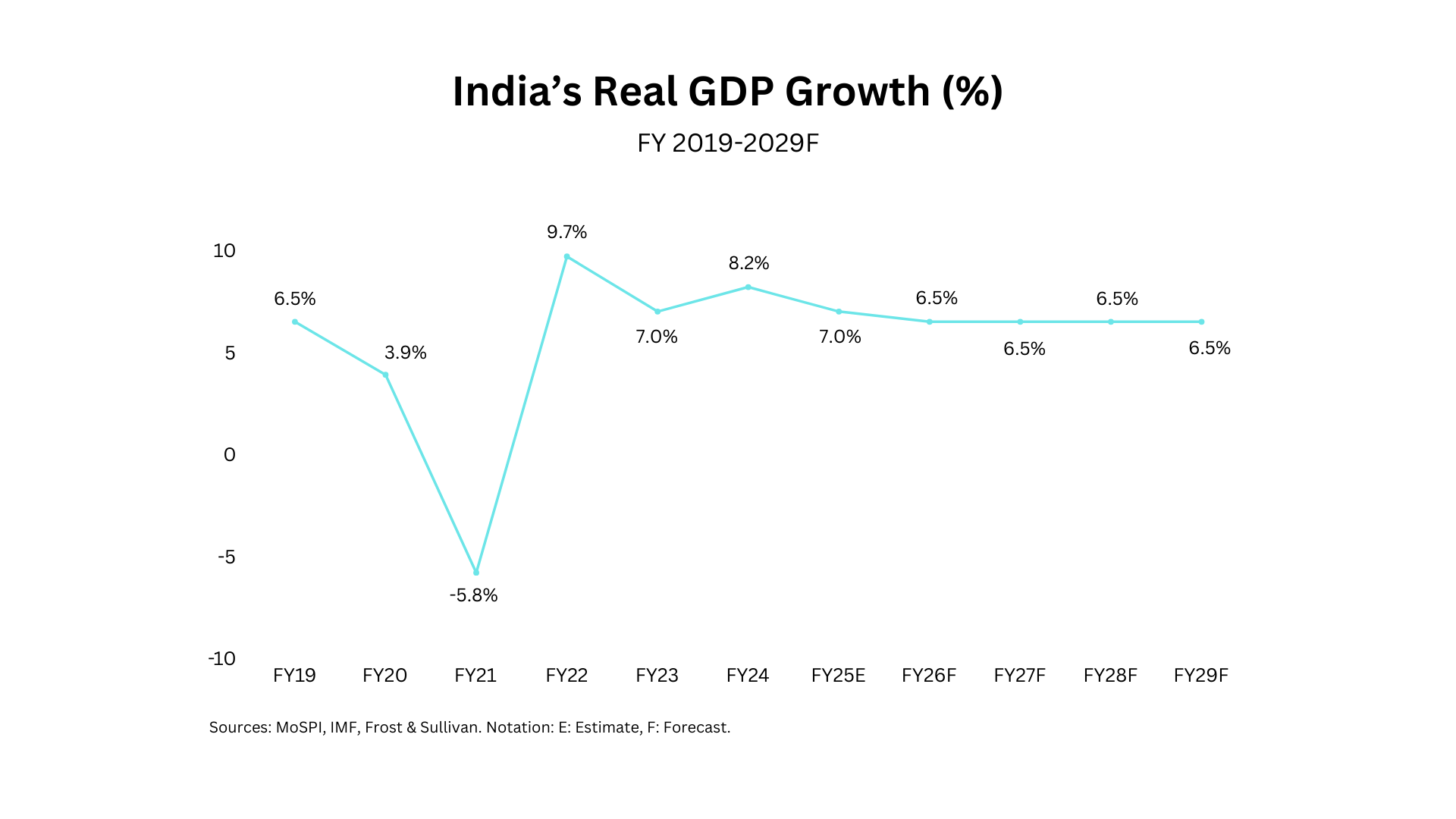
India continues to cement its position as a global economic powerhouse, showcasing robust growth and a promising trajectory. With an impressive real GDP growth of 8.2% in FY2024, India surpassed expectations and solidified its status as a bright spot in the global economy. The country's average annual growth rate is projected at 6.6% between FY2025 and FY2029, with significant milestones on the horizon. India is expected to overtake Japan by 2025/2026 to become the world's fourth-largest economy and surpass Germany by 2030, securing the third spot globally in nominal GDP terms. By the end of this decade, nominal GDP is anticipated to exceed INR 486 trillion, driven by massive consumer spending potential, a cost-competitive talent pool, and strong manufacturing growth.
Key Growth Drivers of India's Economy
Growing Capital Expenditure (Capex)
India has witnessed a remarkable rise in capital expenditure over recent years. Government capex grew at a CAGR of 18.4%, surging from INR 2.4 lakh crore in FY2016 to INR 9.1 lakh crore in FY2024. For FY2025, the capex target is set at INR 11.1 lakh crore, an 11.1% year-on-year increase, accounting for an estimated 3.4% of the total GDP. This continued investment underscores India's commitment to infrastructure and economic development.
Rising Per Capita Income Levels
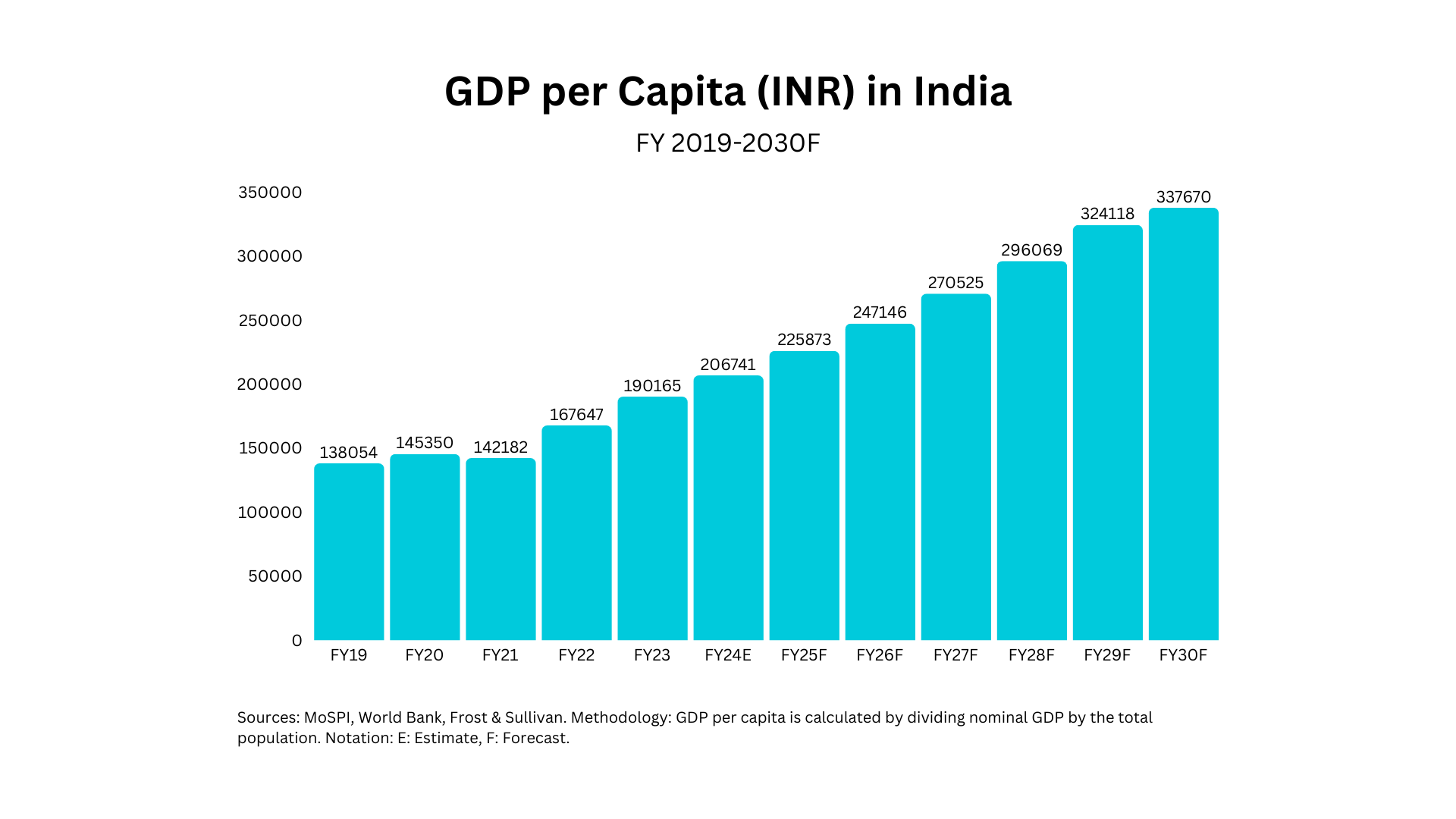
India's GDP per capita reached INR 206,741 in FY2024 (current prices) and is projected to hit ~INR 337,000 by FY2030, growing at a CAGR of 8.5%. This growth is fueled by technological integration, increased foreign and domestic investments, a vibrant startup ecosystem, political stability, and improved business policies. These factors will bolster domestic income levels and, in turn, drive consumer spending.
Demographic Dividend and Youthful Population
In 2024, India's working-age population (15-64 years) accounted for 68% of the total population, with a median age of 29.5 years - significantly younger than China's 39.8 years and Europe's 42.5 years. Comparatively high fertility rates are expected to sustain steady growth in the youth population through 2030. This demographic advantage, coupled with a skilled labor force, positions India for significant growth in sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, construction, mobility, and ICT.
Promising Export Potential
India's export potential is set to soar, backed by the rapid growth of Special Economic Zones (SEZs), expanding export incentives, digital infrastructure development, and public-private partnerships. By the end of this decade, India aims to surpass USD 2 trillion in exports, further solidifying its role as a global trade leader.
Burgeoning Middle Class
India's middle class is set to become the largest in the world, with 1,375 million people by 2040, outpacing China's ~1,250 million, according to OECD projections. Rising per capita incomes and sustained economic growth will enhance middle-class purchasing power, making them a key target market for businesses worldwide. Additionally, robust GDP growth will ensure upward momentum for national disposable income across all income categories.
Expanding Female Labor Force Participation
India's socio-economic landscape is evolving, with increasing female contributions to the workforce. Female labor force participation rose from 23.3% in 2017-18 to 37.0% in 2022-23, driven by rapid growth in knowledge-based sectors, higher literacy rates, and favorable fiscal policies. This trend reflects India's commitment to fostering an inclusive and diverse economy.
Skilling Investments and Multilingual Workforce
India's focus on skilling and reskilling is pivotal for its economic growth. Initiatives like the National Skill Development Corporation's programs and government budgets prioritize upskilling. For instance, the FY2025 Union Budget introduced schemes to skill 20 lakh youth and upgrade 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes. Coupled with India's bilingual and multilingual education system, these efforts enhance India's appeal as a long-term investment destination.
Challenges to India's Macroeconomic Scenario
India's macroeconomic landscape faces a series of challenges that could potentially impact its growth trajectory and financial stability. From currency fluctuations to geopolitical risks, these factors require careful monitoring and strategic interventions.
Vulnerability to US Dollar Appreciation
One of the most pressing challenges is the Indian rupee's depreciation against the US dollar. Since March 2019, the dollar has appreciated by approximately 20.5% relative to the rupee as of March 2024. This trend poses significant challenges for the Indian economy. A stronger dollar adversely affects the country's current account by increasing the cost of imports and reducing the competitiveness of exports. Moreover, dollar appreciation discourages foreign investments in India, as it diminishes the real rate of return for international investors.
Dependence on Strategic Imports
India's heavy reliance on strategic imports further complicates the situation. The economy depends on essential imports like crude oil, minerals, chemicals, and electronics, which are critical for sustaining growth. Any disruption in the supply of these goods - whether due to geopolitical tensions or other reasons - could undermine the country's financial stability. This reliance highlights the need for diversification of sources and a push for self-reliance in critical sectors.
Policy Implementation and Monitoring
The Indian government has made commendable strides in creating a business-friendly environment. This is reflected in India's improved ranking of 63rd in the global ease of doing business index. However, the true test lies in the consistent implementation and monitoring of these policies. Delays, inefficiencies, or negative deviations in policy execution could significantly hamper economic growth and investor confidence. Ensuring seamless execution and regular evaluation is crucial for maintaining the momentum of reforms.
Geopolitical Risks
Geopolitical tensions continue to pose a looming threat, keeping uncertainty levels high. Although India has displayed remarkable resilience amidst these challenges, any escalation - such as conflicts in the Middle East or disruptions in the Red Sea region - could have serious repercussions. Rising logistics costs and potential disruptions in crude oil supplies are particular concerns. These issues could weaken India's export competitiveness and reverse the recent easing of inflation in core and fuel categories. Prolonged geopolitical instability may also compel the Reserve Bank of India to maintain higher interest rates for an extended period, further tightening economic conditions.
Future Outlook
India's macroeconomic landscape reflects a dynamic and resilient economy poised for sustained growth. From rising capital expenditure and increasing per capita incomes to a youthful workforce and expanding middle class, India's growth drivers are well-positioned to shape its future. As the country embraces technological advancements, skilling initiatives, and inclusive policies, it is on track to emerge as a global leader, offering immense opportunities for businesses and investors alike.